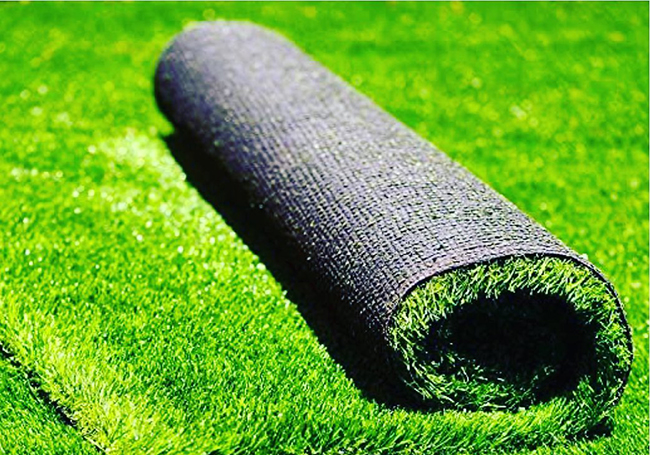
The Consumers Association of Penang calls on the authorities to ban artificial grass as it harms the environment and health.
Plastic grass is a rapidly growing trend with a US$2.4 billion global market.
In Malaysia, it is commonly used in the compounds of homes, buildings and public recreational areas. But there is a lack of awareness of its risks.
Artificial grass can destroy microorganisms in the soil under the grass, which harms surrounding plants, thus hindering biodiversity. Furthermore, due to its composition, it is tough to recycle.
Plastic which does not biodegrade adds strain on the waste sector. And as it breaks down, it releases plastic particles into the environment, making it toxic to humans and wildlife.

The Royal Horticultural Society in the UK recently banned artificial grass from its world-famous flower shows for environmental reasons.
The UK government is urged to introduce an “Ecological Damage Tax” on the import, sale and installation of artificial lawns and grass to address the problem.
Meanwhile, the Adelaide City Council banned artificial turf on verges in 2019 due to urban heating and landfill concerns. According to the Council’s report, the surface temperature of artificial turf is higher than other surfaces, including asphalt and significantly higher than natural turf.
The composition of artificial grass
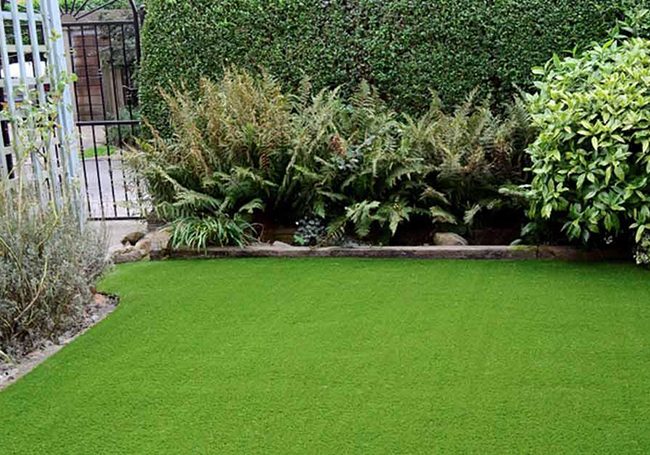

Artificial grass carpet and turf contain three major parts: plastic blades, a backing material that holds the individual blades of artificial grass, and an infill (tiny black crumbs that help support the blades).
Polyethene is the material used to make artificial grass blades. It is the same materials used to make bottles and plastic bags.
Polyethene in solid form is melted and mixed with colours and other chemicals to make it durable and UV resistant. Alternatively, extruded thin nylon sheets via moulds to produce fine fibres to make the grass.
The infill contains particles called butadiene rubber or “crumb rubber” made from synthetic fibres and scrap tyres. The materials in the infill can contain benzene, carbon black and lead, all implicated in cancer.
Links to cancer and injury risks

A 2019 Yale study found 306 chemicals in crumb rubber, 52 of which were classified as carcinogens by the US Environmental Protection Agency.
In 2019 Washington officially revealed that 17 playgrounds in the state had dangerously high levels of lead.
That same year, the Ecology Center in the US tested crumb rubber found on broken rubber surfaces of several playgrounds and found dangerously high levels of lead in some pieces.
In 2007 the California Office of Environmental Health Assessment (OEHHA) simulated interactions children can have after directly contacting artificial turf.
They found five chemicals, including four polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, in the samples tested. One compound, chrysene (a known carcinogen), was present at levels higher than the standard set by OEHHA.
In 2017, 37 out of 51 artificial turf fields in Washington failed safety tests due to hardness scores above 165.
Why artificial grass is harmful and undesirable

According to studies, 50% of rainfall runs straight off artificial lawns and can lead to overflowing drains and flooding. In contrast, natural grass absorbs nearly every drop of water.
The grass is also said to overheat in hot weather as it absorbs heat and can even cause friction burns to children playing on it.
A Loughborough University study found its artificial sports pitch often reached 65 degrees Celsius when the air temperature hit 25 degrees Celsius – almost hot enough to fry an egg.
Plastic turf blocks the soil from burrowing insects such as solitary bees and worms. Fossil fuels such as cured oil and coal are used to produce fake grass, which is detrimental to the environment and wildlife.
It is made by bonding several types of plastics together, making it difficult to recycle and more likely to end up in landfills. Recycling requires the materials to be separated and pure.